INTRODUCTION Oysters are an integral part of many marine ecosystems. They provide food for several species of snails and crabs... Read More
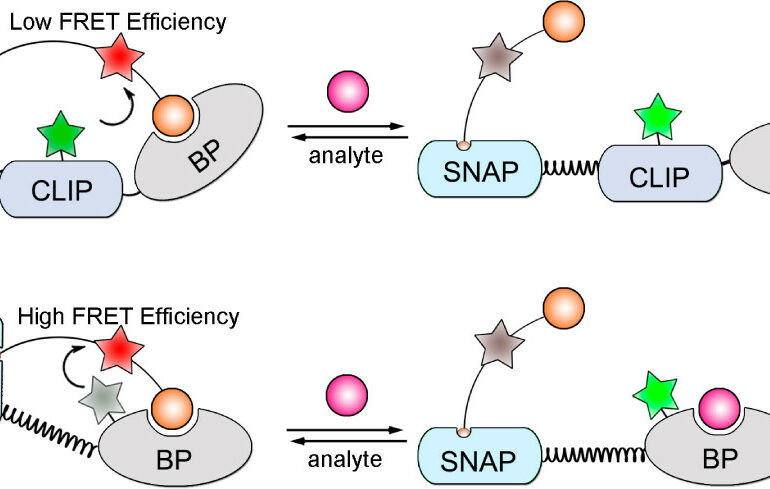
The structure and function of proteins in the human body is largely limited by the number of amino acids that... Read More
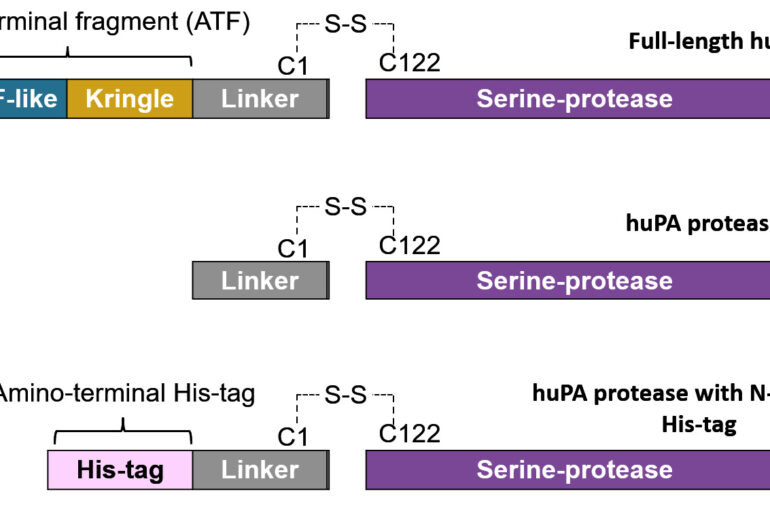
ABSTRACT Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) is a serine protease responsible for cleaving and activating inactive plasminogen to its active form,... Read More
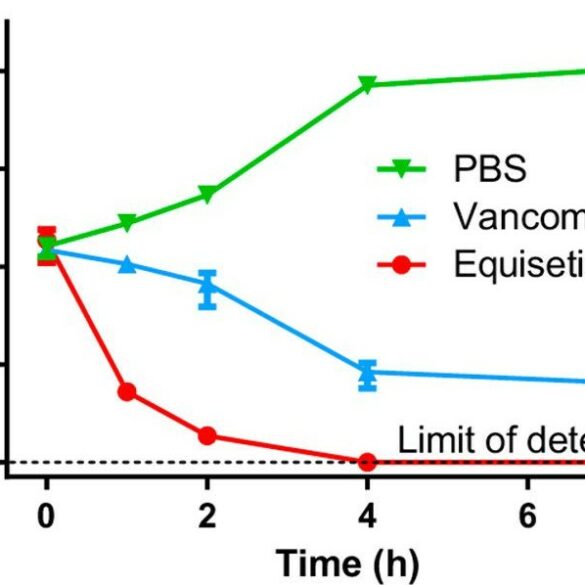
Antibiotics are crucial in protecting humans from a large range of bacterial diseases. Scientists have created several types of antibiotics... Read More
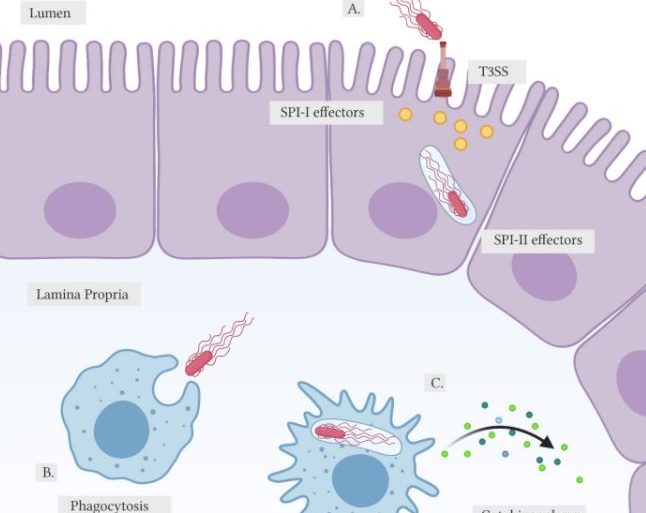
INTRODUCTION Despite many prevention efforts, foodborne illnesses remain a serious global health threat.¹ The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention... Read More
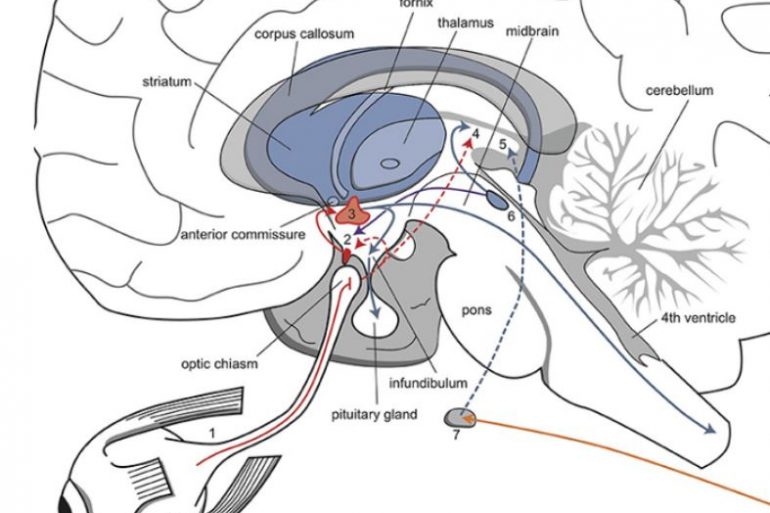
CIRCADIAN RHYTHM 101 The circadian clock is in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the brain.¹ This cluster of nuclei sits... Read More
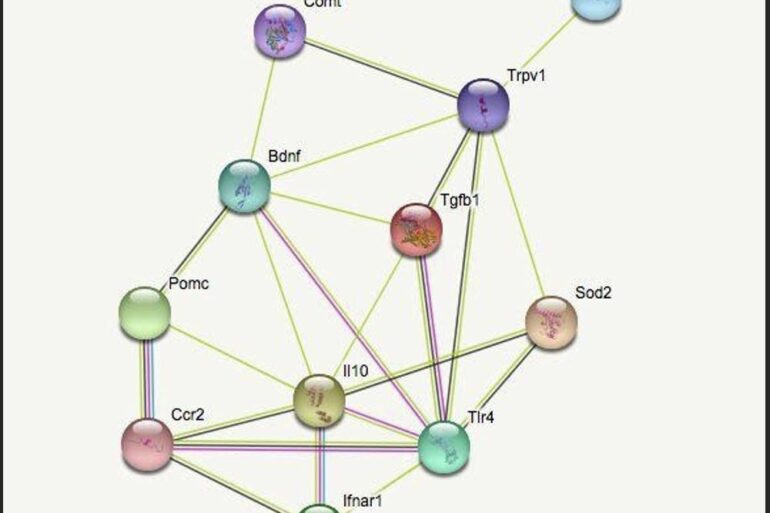
ABSTRACT Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a debilitating autoimmune disease that causes painful inflammation within joint tissue. Despite the success of... Read More
The Division of Biological Sciences Senior Honors Theses Program (BISP 196) is open to undergraduate biology majors who have an... Read More
BACKGROUND Gene therapy has grown in popularity as a potential treatment strategy for a variety of human diseases.¹ Adeno-associated virus... Read More